Understanding Markets
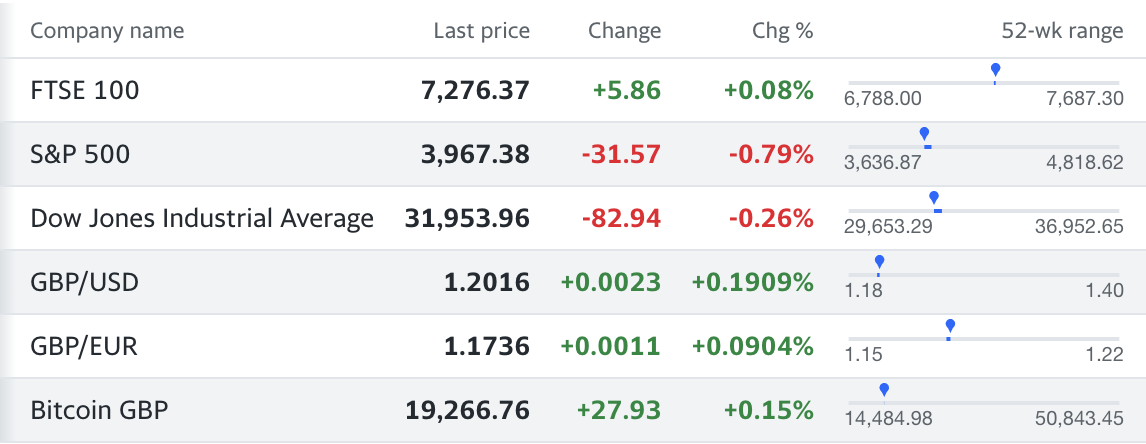
Last Price
The price at that time - time shown under the markets in the newsletter.
Change
The price change in the last 24 hours
Chg %
The price change in the last 24 hours shown as a %
52-wk range
The price range over the last 52 weeks. The blue point shows where the current price lies compared to the last 52 weeks.
FTSE 100
What it is - Financial Times Stock Exchange 100 is an index created in 1984 comprising of the 100 largest companies, by market capitalisation, listed on the London Stock Exchange.
Why it matters? - All the companies in the FTSE 100 are listed on the London Stock Exchange, the main market in the U.K. Companies listed in FTSE 100 account for 81% of the total value of all companies listed in the U.K main market therefore the FTSE 100 is seen as a good gauge of how well the overall UK economy is doing. Although, this is debated as the majority of the companies on the FTSE 100 are international.
How it works - Their combined value is what is tracked as the FTSE 100 but it is also weighted so that the larger the company, the bigger difference it will make on to the FTSE 100 price.
Avg Return - The FTSE 100 has had an average yearly return of around 7.75% since 1984.
S&P 500
What is it? - The Standard and Poor's 500 is a stock market index tracking the stock performance of 500 large companies listed on exchanges in the United States (NASDAQ & NYSE). The index is not simply the 500 largest U.S. companies, there is further criteria for this index, including; a market cap of $13.1+ billion, a U.S. headquarters, and positive earnings for at least four consecutive quarters (they can potentially be removed if this slips).
Why it matters? - Due to its depth and diversity, the S&P 500 is widely considered one of the best gauges of large U.S. stocks, and even the entire U.S. market
How it works? - The S&P 500 is weighted using a market-cap weighting method giving a higher percentage allocation to companies with the largest market capitalisations. This means companies with a higher market cap have a greater impact on the index's total value.
Avg Return - The S&P 500 has had an average yearly return of around 10.5% since 1957.
Dow Jones Industrial Average
What is it? - The Dow Jones Industrial Average, or the Dow as it's commonly known, is an index that tracks 30 large U.S. blue chip stocks. American express, Apple, Coca Cola, Microsoft and Nike are just some of the stocks in the DOW. It was created in 1896 by Charles Dow to serve as a representation of the broader U.S. economy.
Why it matters? - The Dow is one of the oldest and most commonly followed equity indices although with only 30 stocks representing a portion of U.S. corporate titans, it is considered to be an inadequate representation of the U.S. market compared to a broader index such as the S&P 500.
How it works? - The Dow is a price weighted index therefore stocks with a higher price have more impact on the price of the Dow, unlike the S&P 500 which is market cap weighted. The price of the Dow is calculated by the sum of all the stock prices in the index divided by a factor (currently approximately 0.152) this is done so that when any companies in the index undergo a stock split the value of the index is unaffected.
Avg Return - The Dow has had an average yearly return of around 8.7% since 1998.
Exchange Rates
GPB/USD - is the exchange rate from Great British Pounds (£) to the US Dollar ($). In the above example it shows 1.18, this means for every £1 you can get $1.2. On a larger scale, £10,000 would get you $12,000.
GBP/EUR - is the exchange rate from Great British Pounds (£) to the Euro (€). In the above example it shows 1.18, this means for every £1 you can get $1.17. On a larger scale, £10,000 would get you €11,700.
If these exchange rates are high or increasing it can be a good sign the UK economy is doing well, or that the economy using the counterpart is not doing well.
Bitcoin GBP
What is it? - Bitcoin (BTC) is a cryptocurrency created in 2009 by an unknown person, or group, who goes by Satoshi Nakamoto. Bitcoin is a decentralised digital currency that you can buy, sell and exchange directly, without an intermediary like a bank.
Why it matters? - Bitcoin is the words largest and most well known cryptocurrency and the price is an indication on the current demand for decentralised currency. As the demand increases you could see it appearing more and more in day to day life.
How it works? - Bitcoin was created on digital distributing block, known as a blockchain. This records all transactions including date and time, total value, buyer and seller, and a unique identifying code for each exchange therefore acting as a public ledger of cryptocurrency transactions. Satoshi Nakamoto described the need for “an electronic payment system based on cryptographic proof instead of trust.” therefore in this acting ledger, all details of all transactions can be viewed by anyone.